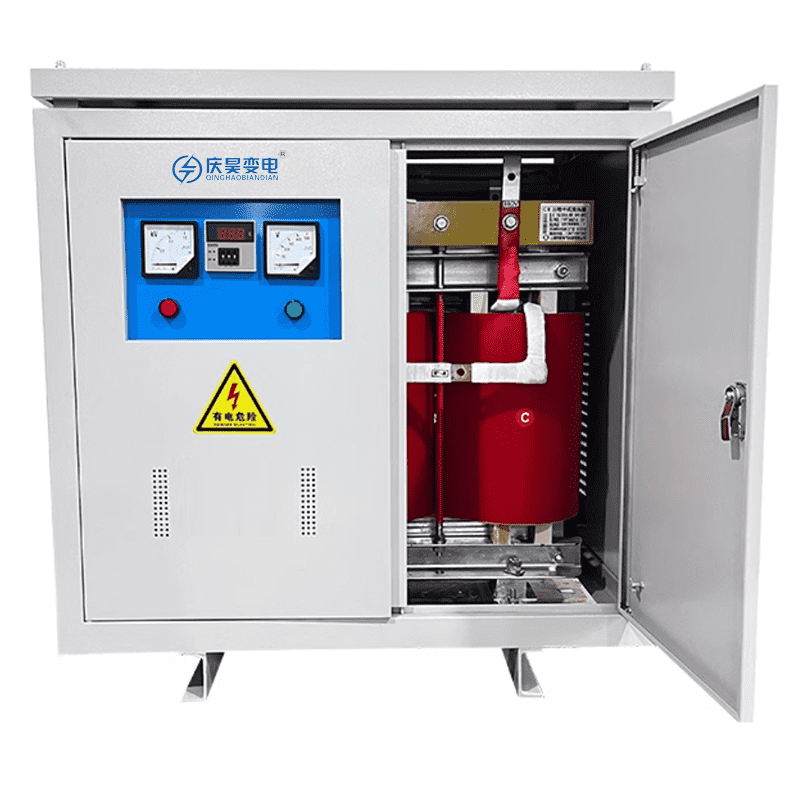
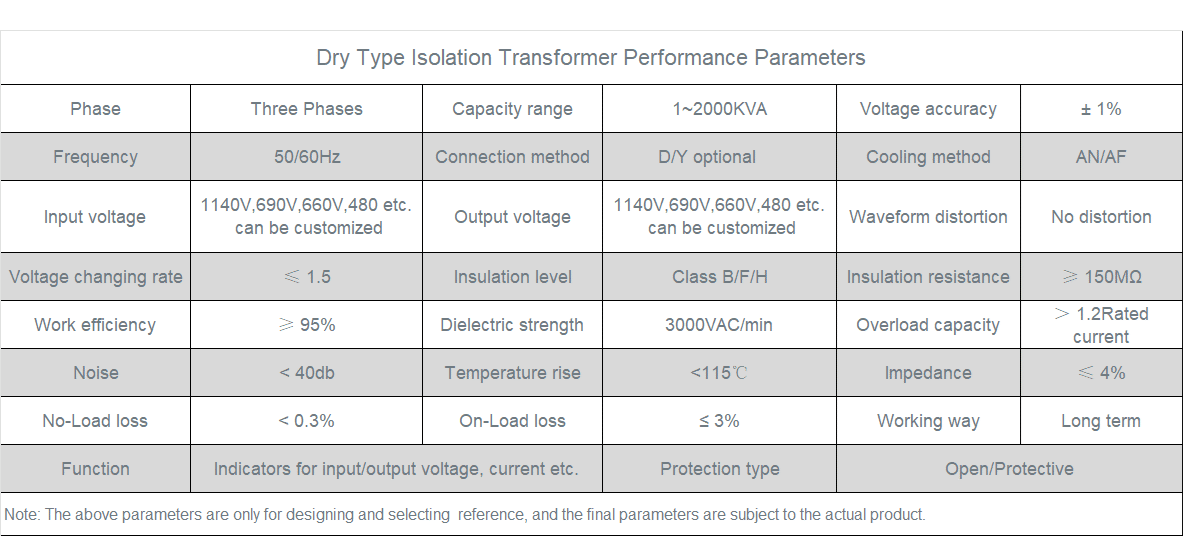
Three-Phase Isolation Transformer
1. Introduction
The three-phase isolation transformer is a specialized transformer with electrically isolated input and output windings. Utilizing electromagnetic induction principles, it achieves voltage conversion and electrical isolation. It is widely deployed in high-safety and high-stability power scenarios such as industrial plants, power plants, airports, high-rise buildings, subways, photovoltaic inverter systems, and wind farm grid connections. Its primary functions include voltage transformation, power supply for lighting systems, motor drives, and rectifier power sources.
2. Features and Advantages
1) Safety Isolation
Shock Prevention: Floating ground design for the secondary winding blocks primary-side fault currents, eliminating shock risks when touching a single wire.
Fault Isolation: Automatically cuts off fault circuits during lightning strikes or short circuits to protect downstream equipment.
2) Efficiency and Environmental Compliance
Low-Loss Design: Utilizes cold-rolled grain-oriented silicon steel and Class H enameled wire, reducing no-load losses by 30%+ with efficiency ≥98%.
Eco-Friendly Process: Halogen-free epoxy resin encapsulation and vacuum impregnation minimize phthalic anhydride emissions, complying with RoHS standards and extending lifespan to ≥20 years .
3) Anti-Interference Capability
Harmonic Suppression: Delta/Wye (△/Yo) or Wye/Delta (Yo/△) configurations filter third-order and odd-order harmonics, purifying grid power.
Shielding Design: Copper foil shielding layers block high-frequency pulse interference, ensuring stable operation of precision devices.
4) Structural Flexibility
Multi-Scenario Adaptation: Supports vertical/protective enclosures and natural/forced air cooling.
Overload Tolerance: Allows 1.2× rated load for 1 hour, accommodating transient peak demands .
3. Application Scenarios
1) Industrial Sector
Equipment Integration: Provides stable power (e.g., 380V→200V) for CNC machines, injection molders, and production lines.
Power Systems: Enables load distribution and electrical isolation in substations/power plants, enhancing grid stability.
2) Construction and Public Facilities
Commercial Buildings: Safeguards power for lighting, HVAC, and elevator systems in malls/offices.
Transport Hubs: Powers emergency systems (EPS/UPS bypass) in subways/airports to prevent blackouts.
3) Specialized Industries
Medical: Isolates power interference for MRI/CT equipment, ensuring diagnostic accuracy and patient safety.
Renewable Energy: Implements grid-device isolation in photovoltaic inverters and wind farms.
4) Emerging Demands
Data Centers: Supplies purified power to server rooms, reducing data packet loss.
Marine/Aerospace: Vibration-resistant construction suits extreme environments, securing navigation/communication systems.
4. Selection Guidelines (Key Parameters)
Load Capacity: Reserve 20% margin beyond actual demand.
Voltage Conversion: Match requirements (e.g., 380V→220V).
Insulation Class: Class H suits high-temperature environments.